This document is for HP LCD displays.
The display panels used in LCD displays have a fixed, predefined pixel format over a set area. For example, if the panel has a predefined area of 1,024 x 768, there are exactly 1,024 pixels in each horizontal line and 768 pixels in each vertical line or 786,432 total pixels.
There are three types of screen resolution configurations on LCD displays:
-
Native resolution or optimal resolution occurs when the screen resolution in the display settings is the same as the predefined area of the display panel. Native resolution is typically the maximum display resolution, and HP recommends using LCD displays at the native resolution.
-
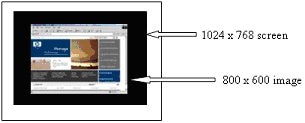
Fixed matrix display uses the number of pixels required for a certain resolution exclusively and typically results in a border or framing effect, but the image size remains unchanged. The fixed matrix display method prevents users from taking full advantage of the display screen size.
-
Scaling uses an expansion technique known as an interpolated algorithm to widen the resolution to fit the entire viewable area of the screen. Scaling requires the manipulation of pixels adjacent to the text to give individual letters a smoother look. The image remains equivalently sized, but the image might appear blurry due to the dithering and loss of data, color, or information. Scaling is the most common method to make full use of the entire screen when operating in a resolution lower than the native resolution.
The default setting for HP LCD displays is the native resolution, but you can change the resolution in the computer display settings.
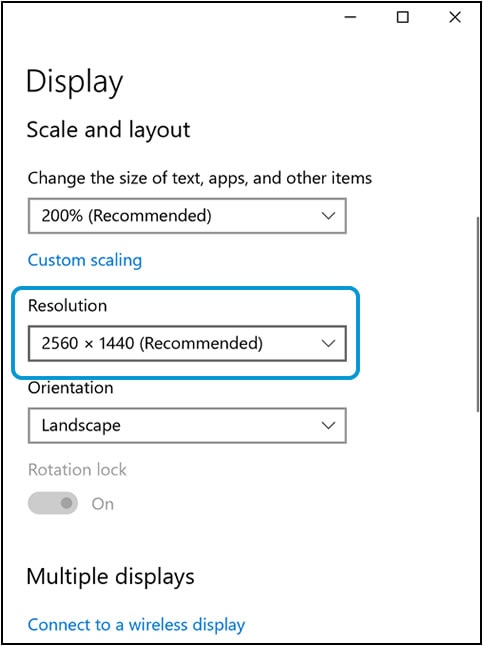
 menu, and then select
menu, and then select